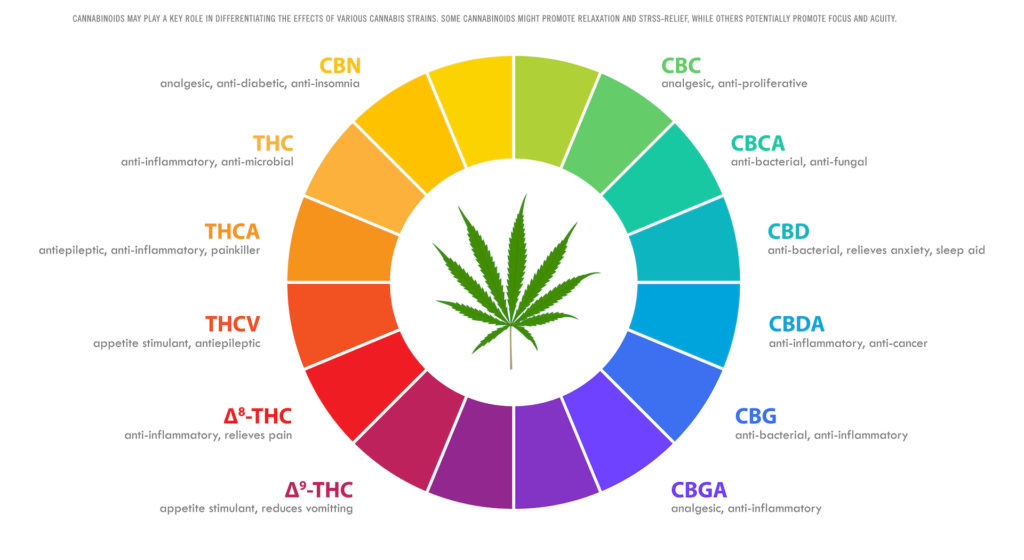
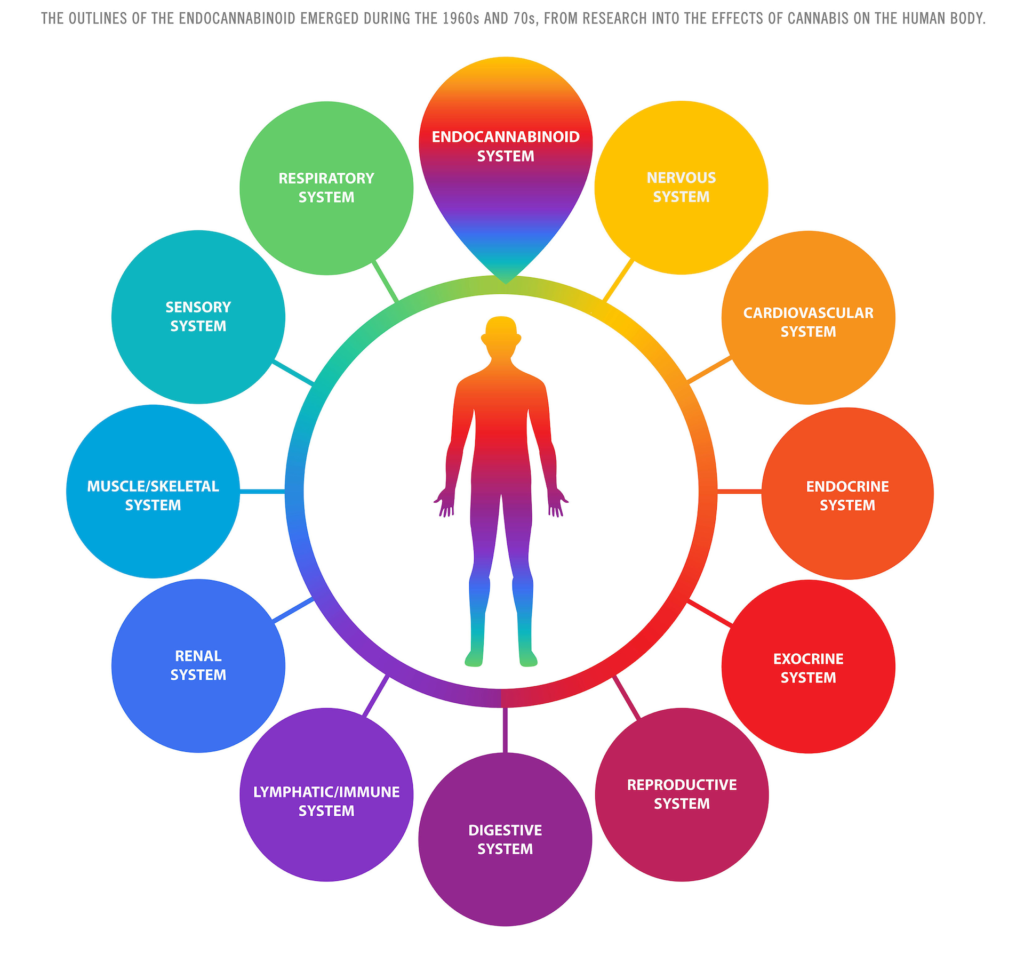
Cannabis is full of active chemical compounds that are responsible for its therapeutic effects and benefits. Some you’re likely familiar with and others you may not have heard of. As research continues to happen, we will continue adding!
Either way, trust us when we say, there’s a lot more to this plant than THC. The cannabinoids and terpenes in the cannabis plant work together to create “the entourage effect”.
What Are Cannabinoids?
Phytocannabinoids — or cannabinoids from plants — interact with several systems in your body, including your digestive system, nervous system, and immune system. They do so by stimulating the receptors of your Endocannabinoid System (ECS), which is responsible for keeping everything in your body balanced.
What Is the ECS?
The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is a communication system within your body that’s responsible for maintaining homeostasis, or metabolic balance. Your brain responds to off-balance situations, like pain or digestive issues, by synthesizing endocannabinoids — cannabinoids produced by the body — that stimulate ECS receptors and restore balance. The 100+ phytocannabinoids in cannabis interact with your ECS in a similar way.
We’ve created this cannabinoid library to give you details about some of the top cannabinoids we’ve explored so far. Check it out below.
Your go-to list of cannabinoids
CBC (Cannabichromene)
Intoxicating: No
CBC is one of the main cannabinoids formed from CBGa (we’ll talk about CBGa below). Little research has been done on this cannabinoid. Still, preliminary studies suggest it may have anti-cancer, anti-inflammation, and pain-relieving properties, and it’s shown promise in the treatment of acne.
CBDa (Cannabidiolic Acid)
Intoxicating: No
CBDa is the predecessor of cannabidiol (CBD). It’s the raw, acidic form of CBD. When the cannabis plant is exposed to sunlight or heat (like from your lighter), the acid burns off, and CBDa becomes CBD — they didn’t cover that in high school chemistry! Preliminary research suggests it may have the potential to treat inflammation, nausea, and even some cancers.
CBD (Cannabidiol)
Intoxicating: No
You’ve probably been seeing more and more CBD products popping up lately. CBD is one of the most popular cannabinoids because of its reported effects and benefits. Anecdotal evidence supports CBD’s pain-relieving and mood-boosting properties. It has also shown the potential to curb the paranoia-inducing effects of THC. Some animal studies suggest it has pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory effects. And within the last few years, the FDA has approved lab-made CBD to treat certain forms of epilepsy.
CBDv (Cannabidivarin)
Intoxicating: No
CBDv is very similar to CBD in structure and effects, but it has one key difference: CBDv has a three-carbon side chain instead of a five-carbon side chain. It’s shown to have properties like CBD, including anti-nausea and anti-epileptic effects, though more research is needed.
CBGa (Cannabigerolic Acid)
Intoxicating: No
Sometimes referred to as “the mother of all cannabinoids,” CBGa is the predecessor of THC, CBD, CBC, and other cannabinoids. When CBGa is exposed to light and heat (in a process called decarboxylation) the acid component of this cannabinoid is burned off. This converts CBGa into CBG, THC, CBD, and CBC. In vitro studies suggest it may help combat complications from diabetes and metabolic diseases.
CBG (Cannabigerol)
Intoxicating: No
“CBG is the “activated” version of CBGa, meaning it doesn’t have the acidic component. Studies suggest the ECS uses this compound to regulate itself. Preliminary research also suggests it has anti-anxiety and anti-fungal effects. And it may help with neurological disorders and certain skin issues.
CBN (Cannabinol)
Intoxicating: No
CBN is what THC turns into when it’s exposed to oxygen. This is why, if you don’t keep your stash in an airtight container, you may start to notice less intense effects. Because CBN is an aged version of THC, it’s usually found in older cannabis. Research suggests it may stimulate appetite and encourage sleep. It’s thought to have antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects.
Delta-8-THC (Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol)
Intoxicating: Yes
Delta-8-THC is similar to the THC you know (which is technically delta-9-THC), but its slight difference in chemical structure means it interacts with your ECS differently than delta-9-THC. This means its intoxicating effects are not nearly as potent.
THCa (Tetrahydrocannabinolic Acid)
Intoxicating: No
THCa is the predecessor of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). It’s non-intoxicating because its acidic component blocks it from binding to your ECS. When the plant is decarboxylated or exposed to light and heat (like from your lighter), it burns off the acid and becomes THC. There’s not much research on this cannabinoid, but some studies suggest it may have antiemetic and anti-inflammatory properties.
THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Intoxicating: Yes
THC, or delta-9-THC, is the cannabinoid that’s responsible for the euphoric high associated with cannabis. Research suggests it can reduce pain, inflammation, and nausea, and it may have anti-tumor properties. Other studies suggest it has the potential to reduce anxiety, but only to a certain extent. Too much THC can induce paranoia.
THCv (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)
Intoxicating: In low doses, no. In higher doses, potentially.
THCv is very similar to THC in structure, but it has a three-carbon side chain instead of a five-carbon side chain. Its effects are not identical to THC’s, and it may even mitigate some of THC’s less desirable effects. Research suggests it acts as an energy booster and appetite suppressant.
LEARN MORE